Notice
suyeonme
[알고리즘/그래프] 강한 연결 요소(Strongly Connected Component, SCC) 본문
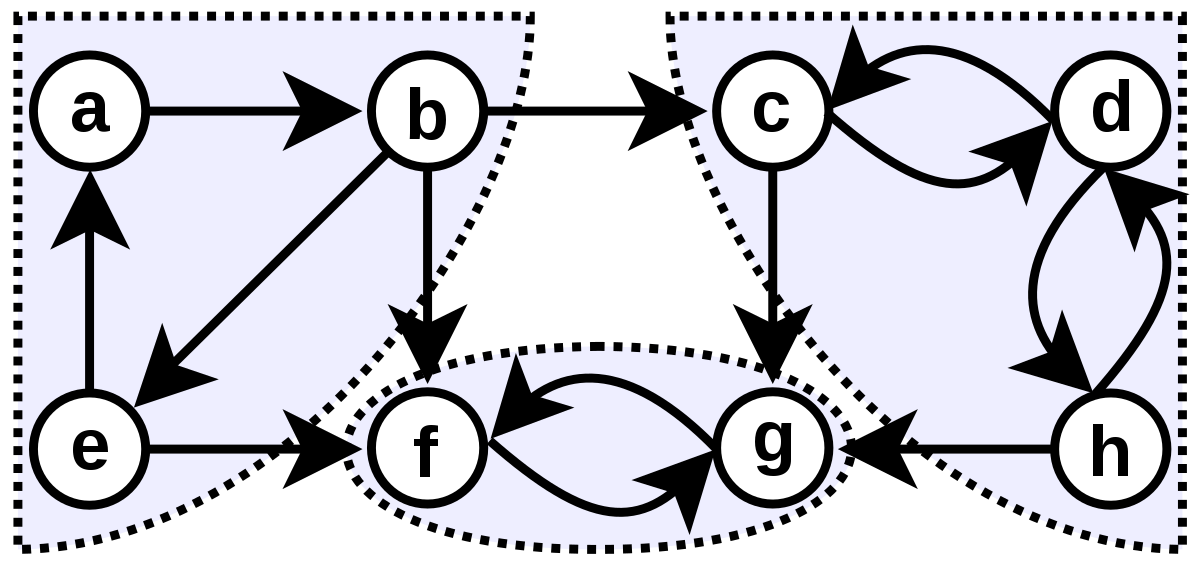
강한 연결 요소(Strongly Connected Component, SCC)란?
그래프안에서 강하게 결합된 정점 집합을 의미한다.
강한 결합 요소의 특징
- 같은 집합에 속하는 두 정점은 서로 도달이 가능하다.
- 사이클이 발생하는 경우 무조건 SCC에 해당한다. 따라서 방향그래프일 때 의미가 있다.
타잔 알고리즘(Tarjan's Algorithm)이란?
타잔 알고리즘(Tarjan's stronly connected components algorithm)은 SCC를 추출하는 대표적인 알고리즘으로 모든 정점에 대해 DFS를 수행하여 SCC를 탐색한다. 이 때 부모 노드로 돌아올 수 있는 경로에 한해서 SCC가 성립된다. SCC 그룹을 정점으로 하여 전체 그래프를 구성한 경우, 사이클이 발생하지 않는 방향 그래프가 되어 위상 정렬(topology sort)을 수행할 수 있다.
* 다른 대표적인 SCC 추출 알고리즘으로 코사라주 알고리즘(Kosaraju's algorithm)이 있다. 코사라주 알고리즘이 구현은 더 쉽지만 타잔 알고리즘이 활용도가 더 높다.
구현 순서
- 그래프 연결 정보를 저장한다.
- 시작 노드에서 DFS를 수행한다.
- 인접 정점을 방문하여 자신을 스택에 넣고 재귀적으로 DFS를 수행한다.
- 인접 정점에 방문했지만 처리중인 경우, 작은 값으로 부모를 갱신한다.
- 부모노드의 DFS가 끝났다면, 자신의 고유값(id)이 스택에서 나올 때 까지 스택에서 노드를 제거한 뒤, scc 배열에 추가한다.
- 만들어진 하나의 scc 배열을 전체 SCC 배열에 추가한다.
구현 코드
public class StronglyConnectedComponent {
static int MAX = 100001;
static int id = 0; // 노드의 고유값
static int[] d = new int[MAX]; // 노드의 고유값
static boolean[] finished = new boolean[MAX]; // 현재 특정 노드에 대한 DFS가 끝났는지 여부
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> SCC = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
static Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 정점의 개수만큼 DFS 실행
static int dfs(int x) {
d[x] = ++id; // 노드마다 고유값 할당
stack.push(x); // 스택에 자기 자신을 삽입
int parent = d[x];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int y = graph.get(x).get(i); // 인접노드
if (d[y] == 0) {
// 방문하지 않은 노드
parent = Math.min(parent, dfs(y)); // 더 작은 값으로 부모값 갱신
} else if (!finished[y]) {
// 현재 처리중인 노드
parent = Math.min(parent, d[y]);
}
}
if (parent == d[x]) {
// 부모노드가 자기 자신인 경우
ArrayList<Integer> scc = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while (true) {
int t = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
scc.add(t);
finished[t] = true;
if (t == x) break; // 자기 자신이 부모인 경우
}
SCC.add(scc);
}
return parent;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int V = 11; // 정점의 개수
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>()); // 그래프 초기화
}
// 그래프 정보 입력
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(2).add(3);
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(4).add(2);
graph.get(4).add(5);
graph.get(5).add(7);
graph.get(6).add(5);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(8).add(5);
graph.get(8).add(9);
graph.get(8).add(10);
graph.get(8).add(9);
graph.get(9).add(10);
graph.get(10).add(11);
graph.get(11).add(3);
graph.get(11).add(8);
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
if (d[i] == 0) {
dfs(i);
}
}
System.out.println("scc의 갯수:" + SCC.size());
for (int i = 0; i < SCC.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(i + "번째 SCC: ");
for (int j = 0; j < SCC.get(i).size(); j++) {
System.out.println(SCC.get(i).get(j));
}
}
}
}'프로그래밍👩🏻💻 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘/그래프] 이분매칭(Bipartite Matching) (0) | 2022.12.04 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘/그래프] 에드몬드 카프(Edmonds-Karp) 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.12.04 |
| [알고리즘/그래프] 위상 정렬(Topology Sort) (0) | 2022.11.07 |
| [알고리즘/그래프] 플로이드 와샬 알고리즘(Floyd Warshall Algorithm) (0) | 2022.11.06 |
| [알고리즘/그래프] 다익스트라 알고리즘(Dijkstra Algorithm) (0) | 2022.11.05 |
Comments